European packaging legislation and the role of the authorized representative



The changes to the Austrian Packaging Ordinance are currently also attracting a great deal of interest among German retailers. The main reason for this is a significant innovation: since 1 January 2023, foreign retailers who ship products to Austria and do not have a branch there must appoint an official authorized representative. However, this requirement is not only valid in Austria; similar regulations also exist in other EU countries. We shed light on the countries in which the appointment of an authorized representative is required for shipping and what consequences this has for you.
As an online retailer who ships goods across German borders, you may be faced with the question of how to comply with the different packaging laws in Europe. This question is complex, as the EU Packaging Directive is implemented differently in each EU country. This leads to a variety of processes and requirements. Many of these laws have recently been revised and additional regulations have been added. An increasingly common aspect in these laws is the need to appoint an authorized representative for foreign distributors.
Definition and procurement of an authorized representative
A proxy is a person or organization authorized by an official power of attorney to perform specific tasks on behalf of another person. This power of attorney is a written document that confirms that the person or organization in question (your proxy) may act on your behalf. In most countries, any natural or legal person who is resident in the country in question, has a local address and has been appointed by means of a notarized power of attorney can act as proxy.
The search for a suitable proxy can be complicated. We offer a licensing service, through which we can take care of all of the compliance in the respective countries for you.
Requirement of an authorized representative in various countries
For shipping to certain countries, including Austria, Slovenia, Portugal, Greece and Slovakia, it is necessary to appoint an authorized representative. Let’s take a closer look at the requirements in these countries.
Austria
Since the Packaging Ordinance in Austria was updated on January 1, 2023, retailers who do not have a place of business in Austria must appoint an authorized representative for shipments to this country. This regulation affects you if you deliver packaging materials to consumers in Austria. As a foreign company, you must ensure through your authorized representative that you comply with the requirements of the Austrian Packaging Ordinance. Since January 1, 2023, it is no longer possible for companies that are not based in Austria to carry out licensing independently.
Required Measures:
- Appointment of an authorized representative in Austria.
- Keeping records of the packaging materials distributed in Austria.
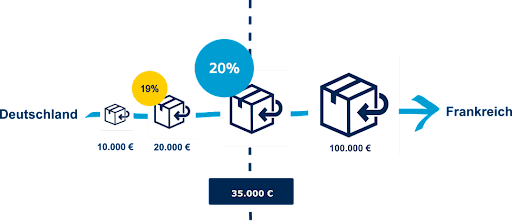
- Transmission of the packaging quantities to your authorized representative (annually up to 1,500 kg, quarterly up to 20,000 kg, monthly over 20,000 kg).
- Payment of the fees for the authorized representative and for disposal.
Slovenia
In Slovenia, an important regulation based on an amendment to the Environmental Protection Act came into force on April 24, 2021. This regulation, issued by the Slovenian government, stipulates that all foreign companies that sell packaging on the Slovenian market must appoint a local authorized representative. This authorized representative is then responsible for ensuring compliance with the take-back obligations. This regulation applies regardless of the quantity of packaging put into circulation. Please note that an additional environmental levy must be paid from an annual quantity of 15 tons.
Required Measures:
- Appointment of an authorized representative in Slovenia.
- Keep accounts of the packaging quantities put into circulation in Slovenia.
- Quarterly reporting of packaging quantities to the authorized representative.
- Payment of disposal fees (licensing) and fees for the authorized representative.
Portugal
In Portugal, the environmental authority APA has tightened the regulations on packaging with effect from January 1, 2022 by introducing the mandatory appointment of an authorized representative for all packaging. This regulation particularly affects non-Portuguese manufacturers who sell their products directly to private end consumers in Portugal. In this case, all relevant obligations must be fulfilled by the authorized representative.
Required Measures:
- Appointment of an authorized representative in Portugal.
- Documentation and tracking of the quantities of packaging put into circulation in Portugal.
- Annual reporting of packaging quantities to the authorized representative.
- Payment of the fees incurred for the authorization and for the take-back system.
Greece
A new law came into force in Greece on July 1, 2021, replacing the previous regulations from 2001. Since then, non-Greek retailers who ship goods to Greece are also obliged to register with the Greek take-back system. For companies without a registered office in Greece, the appointment of an authorized representative is also required.
Required Measures:
- Appointment of an authorized representative in Greece.
- Documentation of the quantities of packaging put into circulation in Greece.
- Annual transmission of the packaging quantities to the authorized representative.
- Payment of the costs incurred by the authorized representative and for disposal.
Slovakia
As of January 1, 2022, foreign mail order companies that do not have a registered office in the Slovak Republic must process their obligations via an authorized representative. This authorized representative assumes responsibility for fulfilling all legal obligations and acts on behalf of the trader.
Required Measures:
- Appointment of an authorized representative in Slovakia.
- Documentation of the quantities of packaging placed on the Slovakian market.
- Quarterly reporting of packaging quantities to the authorized representative.
- Payment of the costs incurred by the authorized representative and for disposal.
Spain
A new law came into force in Spain on 27 December 2022, replacing the previous regulations. Since then, foreign traders without a registered office in Spain are obliged to appoint an authorised representative.
Measures required:
- Appointment of an authorised representative in Spain.
- Documentation of the quantities of packaging put into circulation in Spain.
- Annual transmission of the packaging quantities to the authorised representative.
- Payment of the costs incurred by the authorised representative and for disposal.
Summary and outlook
Packaging legislation remains an important and dynamic topic. The trend of more and more countries requiring the appointment of an authorized representative for foreign distributors is likely to continue. With the constant revision of legislation and the introduction of new control mechanisms in various countries, it remains an area where up-to-date information is crucial. We will continue to update this post to keep you up to date with the latest developments and requirements.

LIZENZERO.EU makes packaging compliance in Europe very easy.
Do you ship your products to different countries in the EU? Many different legal requirements and obligations can make the whole thing quite complicated – but don’t worry, we’ll do it for you. How do we do it? With our licensing service, we take over all obligations for you by power of attorney. Sounds good? We’ll be happy to advise you.
For shipping to Germany, you can easily fulfill your packaging obligations yourself via Lizenzero.de.
EUDR regulation postponed: What changes are coming?
Die Europäische Union hat in den letzten Jahren einen umfassenden Regulierungsrahmen geschaffen, der elektronische Marktplätze vor neue Herausforderungen stellt. Kontrollpflichten zielen so zum Beispiel darauf ab, Verbraucherschutz, Produktsicherheit und faire Handelsbedingungen zu gewährleisten. Doch was bedeutet das konkret? Welche Verantwortung tragen elektronische Marktplätze, und welche Auswirkungen hat das auf Händler:innen, die diese Plattformen nutzen?
Control obligations for electronic marketplaces in the EU
In recent years, the European Union has created a comprehensive regulatory framework that poses new challenges for electronic marketplaces. Control obligations, for example, aim to ensure consumer protection, product safety and fair trading conditions. But what does this mean in concrete terms? What responsibilities do electronic marketplaces have and what impact does this have on retailers who use these platforms?
Focus PPWR: New EU regulations for packaging?
The European Union is pursuing ambitious plans to promote the sustainability of packaging. This is particularly evident in the draft Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), which was published in November 2022. This sets out binding requirements for packaging and packaging waste on the European market and goes beyond the previous EU directive. As a regulation, the PPWR will apply uniformly in all 27 EU member states, which, in contrast to previous directives, leaves less scope for national adjustments.